Chapter 12 Liquids & Solids
advertisement

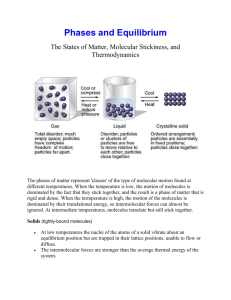
Q: What happens at high altitudes, like Denver & Mt Everest? Below sea level altitudes? •___________________ •Most space between molecules •___________________ •Most compressible Kinetic Molecular Theory: ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ • ____________: imaginary gas that _____________ _______________of the Kinetic Molecular Theory. Fundamental assumptions of an Ideal Gas: 1.) __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ Gas molecules are much further apart than in liquids & solids. Most of a gas is empty space. 2. ) ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 3. ) Gas particle collisions are ________________ Elastic means: ____________________________________________. Collisions are between gas particles, or against the container walls. ALSO: The Average Kinetic Energy (KE ) of the gas depends on Temperature (T). ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Interested in the average KE because not all particles are moving at the same speed, even though they are all at the same Temp. Applications of Kinetic Theory of Gases. 1.) _____________: gases will always spread out to fill any space they are in. 2.) Fluids (Gases & Liquids): gas particles can move past each other without hindrance (fluidity). 3.) Low Density: ______________________________ __________________________. therefore less mass in the same volume 4.) Compressibility: ___________________because of lots of empty space. 5.) Diffusion: _________________________________ ______________________________________. Pressure: ____________________________on a surface. It is the result of collisions by gas particles (Force) against any surface or section of a container wall (Area), Thus, _______________________________________ _________________ on the inside of the walls. To decrease pressure you can increase the area, lower the force ___________________________________________ _______________________, therefore we have a gas pressure. The atmosphere: the gases of the atmosphere (N2 + O2 = 99%), exert pressure on the Earth’s surface. This pressure value is known as _______________________and: Atmospheric Pressure = _____________ = _______________ = ____________(this is the unit we will use) Measuring pressure Barometer: ______________________________ _______________________ (Early 1600’s by Evangelista Torricelli) Mercury: pushed down by gravity… pushed up by atmospheric pressure until it hits equilibrium… _______________ The pressure of the atmosphere (101.3kPa) is enough to balance the weight of Mercury (Hg) that is 76cm high. ( = 29.9 in.) _______________________________________ If the pressure of the atmosphere drops, then it can’t support as much Hg, so height level drops as well. Because we know that pressure depends on temp it is also clear that the height of Hg Temp. Units: The pressure of the standard atmosphere (101.3kPa) has a special unit – atmospheres (atm.) ______________________________________________ is also known as ___________________________ When giving details about gases, __________________ _______________________. The standard temperature used is 0ºC (32oF) So there is a __________ _________________________ (aka STP) and STP = ___________________ Scott Weiland (vocals) now of Velvet Revolver and his brothers in Stone Temple Pilots Diffuse ______________ Have Surface Tension (we’ll come back to this) Form Solids Evaporation: process in which liquid molecules at the surface have enough KE to leave (escape) and become gas molecules. 3 ways to speed up evaporation: 1) _______________________________________ 2) _____________________ 3) ______________________ Consider a closed flask containing some water at room temperature The ______________water molecules at the surface leave and become a gas - called ________________. At the same time, some of the __________ ___________________ molecules hit the surface and become __________. The ________________ ____________________ ___________________. i.e. it adds its own Partial Pressure to the air’s pressure. Eventually, the # of molecules turning into vapor = # of molecules turning into liquid. This is called _______________. At equilibrium, ______________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ If you keep increasing the Temp., the vapor pressure will increase until it equals the atmospheric pressure. At this temperature __________________ __________________________ This special Temp. is known as the _________ __________________ Now heat the liquid water. The KE of the molecules increases, which means more liquid molecules will become vapor. The system reaches a new equilibrium Liquid + Heat Vapor ________________________________ As you cool the liquid the kinetic energy decreases which means more of the molecules become liquid Liquid + Heat Vapor ________________________________________________ ___________________________________________ If you decrease the heat enough you will reach the point where the liquid becomes solid… _____________________________ Forming a Solid! As Temp decreases, the average KE also decreases and we get : Freezing: ________________ _________________________ _________________________ _____________(i.e. cooling) •Least movement •Least compressible •Lowest Energy Solids The strong intermolecular forces hold the particles of a solid in _____________ ______________, with only vibrational movement around fixed points, causing the molecules to have an ordered arrangement. Crystalline solids: atoms arranged in ________ _________________ _________________ Amorphous solids: atoms _________________ e.g. glass, plastics, wood… Properties of Solids Definite Shape and Volume High Density; Low compressibility Low Rate of Diffusion Melting: physical change of a solid to a liquid by adding heat . _______________ _________________________________ . When substances form solids, at whatever Temp that may be, they mostly form a ___________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________.