environmental science ii final exam review unit 2: energy
advertisement

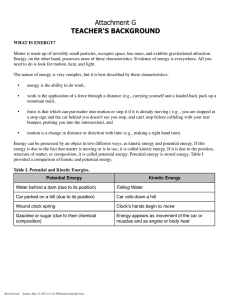
ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE II FINAL EXAM REVIEW UNIT 2: ENERGY • Final Exam will be on Wednesday June 10, 2015 • The final exam is worth 20% of your final grade for the course • Please bring a pen or pencil to the exam with you. Absences: Excused absence- you will take it on the day you return Unexcused absence- you will receive a 0 *****During the exam, if your cell phone or any electronic device is on your person, you will receive a 0!!!***** • All energy comes from the SUN!!!!! • Energy needs have increased over time • more people, more technology, more cars, more products Renewable: energy resource that will not run out in the near future Nonrenewable: energy resource that will run out in the near future FOSSIL FUELS • Made from the remains of living things • Pros• convenience, • reliable, • cost-effective • Cons• Nonrenewable • pollution- Carbon Dioxide, Global warming • Habitat destruction 1. Coal • Made from remains of plants through the process of sedimentation • Solid • Used to generate electricity Stages of Coal Formation • • • • peat- not true coal, low carbon, low energy Lignite- first true form of coal, 40% carbon Bituminous- 85% carbon, most abundant in the US Anthracite- 95% carbon- very hard Mining • Pollution- air, land, water • Reclamation: a process that reduces the amount of damage mining does to an ecosystem 2. Petroleum (oil) • Made from remains prehistoric organisms in shallow seas through the process of sedimentation • Liquid • Used for gasoline, heating, lubricants 3. Natural Gas • Made from remains of microorganisms through the process of sedimentation • Used to generate electricity Fracking • Fracking fluid- water, sand, chemicals • Shale rock formation- one in upstate New York • Pros: rely less on foreign countries for oil, cheaper than oil, abundant in the US, monetary value for landowners, creates jobs • Cons: contamination of water, breaking up habitats, industrialization of residential areas, decrease real estate value 1. Nuclear: • Where it comes from: the nucleus of an atom • How is it obtained? Splitting an atom • What is it used for? To generate electricity • Advantages: no carbon emissions, • Disadvantages: disposing of radioactive waste, nonrenewable 2. Solar: • Where it comes from: sun • How is it obtained? Solar panels, PV cells • What is it used for? Generate electricity • Advantages: no air pollution, renewable • Disadvantages: expensive 3. Wind • Where it comes from: wind • How is it obtained? Wind turbines to convert energy to mechanical energy • What is it used for? Generate electricity • Advantages: no air pollution, renewable • Disadvantages: expensive to set up, damage to birds 4. Geothermal: • Where it comes from: heat within the earth • How is it obtained? A geothermal system underground that brings heat to the home in the winter and removes heat in the summer • What is it used for? Heating homes • Advantages: no pollution, renewable • Disadvantages :expensive • Iceland runs exclusively on geothermal energy