RELIGION
advertisement

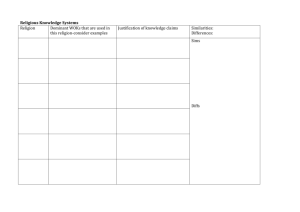
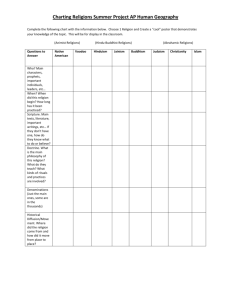
RELIGION • Religion is a social institution involving beliefs and practices based upon a conception of the sacred. • The sacred is that which is defined as extraordinary, inspiring a sense of awe, reverence and even fear. In distinction, the profane consists of ordinary elements of everyday life. • Religions involve ritual, formal ceremonial behavior. • Sociology can investigate the social consequences of religious activity, but can never assess the validity of any religious doctrine because religion involves faith, belief anchored in conviction rather than scientific evidence. Theoretical Analyses Structural-functional analysis • Durkheim understood religion as the symbolic celebration of the power of society over the individual. • Totems are objects in the natural world collectively defined as sacred. • Durkheim noted three major social functions of religion: a. Social cohesion. b. Social control. c. Providing meaning and purpose. Criticism- downplays the dysfunctions of religion. Social Conflict • Marx noted that religion tends to legitimize inequality and the status quo. • It also endorses patriarchy. Does God Favor Males? Religion and Social Change • Max Weber’s Protestant ethic thesis is an important example of how religion can promote social change, in this instance the growth of capitalism. • Liberation theology is a fusion of Christian principles with political activism, often Marxist in character. It has been important in much of Latin America. Types of Religious Organization • A church is a type of religious organization well integrated into the larger society. There are two types of churches. a) An ecclesia is a church that is formally allied with the state. b) A denomination is a church, independent of the state, in societies that accept religious pluralism • a) b) c) d) A sect is a type of religious organization that stands apart from the larger society. They display the following characteristics: They are less formal, more emotional, less intellectualize. Their leaders display charisma. They rely on active proselytization, recruiting many members through a process of conversion. They usually attract lower-class members • A cult is a religious organization that is substantially outside the cultural traditions of a society. World Religions • Christianity is the world’s most widespread religion—monotheistic • Islam. Moslem beliefs center around the “five pillars of Islam.” • Judaism is the smallest of the world religions. It centers around the concept of the covenant • Hinduism is the oldest of the world’s great religions and is located principally in India. • Buddhism also arose in India • Confucianism was the state religion of China • Secularization is the historical decline in importance of the supernatural and the sacred. • Civil religion is a quasi-religious loyalty binding individuals in a basically secular society. • There has been a marked revival of fundamentalist-a conservative religious doctrine that opposes intellectualism and worldly accommodation in favor of restoring traditional, other-worldly spirituality. Fundamentalism is distinctive in the following ways: • a. interpret the scripture literally. • b. reject religious pluralism. • c. pursue the personal experience of God’s • presence. • d. opposes “secular humanism.” e. endorse conservative political goals