Data Modeling Case Study
advertisement

Relationships among Access Database Objects
Database Application
Form
Report
Tables
Query
(View)
Basic Database Objects
SQL:
Structured Query Language
RDBMS: Relational Data Base
Management System
DBA: Data Base Administrator
DB designer/Data modeler
•
•
•
•
A saved SELECT query is officially called a View in SQL.
QUERY in Access can be SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE.
You can create a query against a table or a query.
You can create a form or report against a table or a query.
-1-
Database:
Tables, Columns, Rows,
Primary Keys, Foreign Keys
and Relationships
Potential relational database
for Coca-Cola Bottling Co.
-2-
Multiple (Dual) Perspectives
We use
this data
DATA
ACME
Enterprise
We do
these things
CRUD
SQL Operations
Insert
Update
Delete
Select
ACTIVITY
HIRE
EMPLOYEE
PAY
EMPLOYEE
Create
Update
Delete
Read
User
Interface
App.
......
......
....
....
EMPLOYEE
PROMOTE
EMPLOYEE
FIRE
EMPLOYEE
Data
Process
-3-
Data Model (Entity Relationship Diagram)
Member
Order
sells;
is sold on
Product
placed by;
places
Member
is enrolled under;
applies to
established by;
established
generates;
generated by
is featured in;
features
Agreement
Promotion
sponsors;
is sponsored by
Club
-4-
Data Modeling Case Study
The following is description by a pharmacy owner:
"Jack Smith catches a cold and what he suspects is a flu virus.
He makes an appointment with his family doctor who confirm
his diagnosis. The doctor prescribes an antibiotic and nasal
decongestant tablets. Jack leaves the doctor's office and drives
to his local drug store. The pharmacist packages the
medication and types the labels for pill bottles. The label
includes information about customer, the doctor who prescribe
the drug, the drug (e.g., Penicillin), when to take it, and how
often, the content of the pill (250 mg), the number of refills,
expiration date, and the date of purchase."
Please develop a data model for the entities and
relationships within the context of pharmacy. Also
develop a definition for "prescription". List all your
underlying assumptions used in your data models.
-5-
5
Northwind Database
-6-
6
A Business Form
-7-
7
An Informal Example of Normalization
• A CUSTOMER ORDER contains the following information:
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
OrderNo
OrderDate
CustNo
CustAddress
CustType
Tax
Total
one or more than one Order-Item which has
•
•
•
•
•
ProductNo
Description
Quantity
UnitPrice
Subtotal.
-8-
8
Solution
Unnormalized table
(OrderNo, OrderDate, CustNo, CustAddress, CustType, Tax, Total,
1{ProductNo, Description, Quantity, UnitPrice,Subtotal}n)
Remove repeating group
1st NF
(OrderNo, ProductNo, Description, Quantity, UnitPrice, Subtotal)
Remove partial FD
2nd NF
(OrderNo, OrderDate, CustNo, CustAddress, CustType, Tax, Total)
Remove transitive FD
(OrderNo, ProductNo, Quantity, UnitPrice, Subtotal)
(ProductNo, Description, UnitPrice)
3rd NF
(OrderNo, OrderDate, CustNo, Tax, Total)
(CustNo, CustAddress, CustType)
-9-
9
SQL Select and Query Design in Access
SELECT COURSE.C_ID, COURSE.TITLE, COURSE.FEE
FROM COURSE
WHERE (((COURSE.FEE)>250 And (COURSE.FEE)<=350))
ORDER BY COURSE.FEE DESC;
- 10 -
JOIN and Aggregation Function
Show students ID, name, and GPA
SELECT STUDENT.S_NO, STUDENT.NAME,
Round(Avg(REGISTRATION.GRADE)*100)/100 AS AvgOfGRADE
FROM STUDENT INNER JOIN REGISTRATION ON STUDENT.S_NO =
REGISTRATION.S_NO
GROUP BY STUDENT.S_NO, STUDENT.NAME;
Or Format(Avg(REGISTRATION.GRADE), "###.00") AS AvgOfGRADE
- 11 -
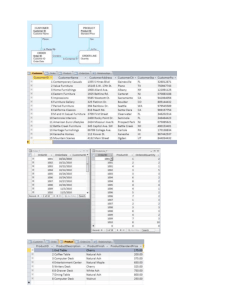
Database(Access) vs. Spreadsheet (Excel)
Features
Database
Excel
Multi-user concurrent
access/update to the data
Volume of the data
Complex relationships of
various data
Calculation /formula among
various data items
Business graph capability
Applications development
tools
- 12 -
http://www.oracle.com/tools/jdeveloper/documents/jsptwp/index.html?content.html
Auction Web
Site's Data Model
- 13 -