Greek Mathematics
advertisement

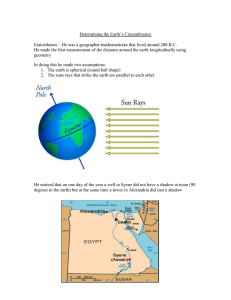
Greek Mathematics Mikaela and Akila The History of Math • • • • • Mathematics began in the 6th century BC Pythagoras coined the term mathematics, which came from the word mathema which means "subject of instruction" Greeks: refined the methods and expanded the subject matter. Chinese: created the place value system. India: Hindu-Arabic numeral system and the rules for the use of its operations From ancient times to the Middle Ages, bursts of mathematical creativity and stagnation Since the Renaissance, new mathematical developments, interacting with new scientific discoveries, were made at an increasing pace that The Theorem of Thales • An angle inscribed in a semicircle is a right angle • OA=OB=OC, so triangles OBA and OBC are isosceles. • A+(A+B)+B=180 2A+2B=180 2(A+B)=180 (A+B)=90 The Pythagoreans • • • Group led by Pythagoras Credited with discovery of irrational numbers Not many people are sure of who found each discovery-- all credit goes to the leader The Discovery of Musical Law • • • • • • Pythagoras was looking to determine interval ratios in music Using lyre and monochord, he stopped the string exactly in the middle and produced an octave ratio of 1:2 The universe is a vast lyre Speed of vibration and size of the sound producing body Sound is produced by a vibration in the air Vibrational frequency of string is inversely proportional to length Eratosthenes • • • • (276-194 BC) Greek mathematician, geographer, and astronomer Noted for devising a map system based on latitude and longitude lines and computing the size of the Earth. 200 BC- thought to have coined or to have adopted the word geography. Eratosthenes Experiment • • • 240 BC Used trig and knowledge of the angle of elevation of the sun at noon in Alexandria and Syene to calculate the Earth's circumference Assumed that the Earth is spherical and that the sun is so far away that its rays can be taken as parallel. Some Definitions Tropic of Cancer: one of the five major circles of latitude that marks maps of the Earth. The current latitude is 23° 26′ 22″ north of the Equator. Local noon: when the sun is the highest in the sky; not necessarily 12 pm on the clock. Solstice: an astronomical event that happens twice a year when the tilt of the Earth's axis is most inclined toward or away from the sun. In the northern hemisphere, summer solstice: around June 21 and winter solstice: around December 21. Just know... What matters for the experiment is the fact that on the summer solstice, local noon, the sun rays are just overhead (at a right angle to the ground) on the Tropic of Cancer. Experiment • • • • He used a vertical stick and measuring the shadow to find that in his hometown of Alexandria, the angle for elevation of the sun would be 83 degrees. He then assumed that Alexandria was due north of Syene, and he used geometry of parallel lines to find that the distance from Alexandria to Syene must be 7/360 of the total circumference of the Earth. The distance between the cities was known from caravan travellings to be about 5,000 stadia. His value for the circumference corresponds to between 39,690 km and 46,620 km. Euclid of Alexandria • • • • • • Greek mathematician 300 BC Father of Geometry His 13 volume Elements was used as a textbook in almost unchanged form for more than 2000 years, and is still a basic source. o It deals with plane and solid geometry, proportion, and properties of numbers. He is known to have conducted a school of mathematics in Alexandria during the reign of Ptolemy I. The first printed edition of the Elements (1482) was in Latin, translated from Arabic. o Sir Henry Billingsley's translation (1570) was the Euclid's Algorithm • A way to find the greatest common divisor of two positive integers. Example: a=210;b=45 • • • • Divide 210 by 45, and get the result 4 with remainder 30, so 210=4·45+30. Divide 45 by 30, and get the result 1 with remainder 15, so 45=1·30+15. Divide 30 by 15, and get the result 2 with remainder 0, so 30=2·15+0. The greatest common divisor of 210 and 45 is 15. a=qb+r Heron • • • • • • • Greek mathematician, scientist, and inventor Renowned for his works in mechanics, mathematics, and physics. Born in Egypt in the year 20 Died in the year 62 Most of his works accomplished in Alexandria, Egypt. Well known for his studies in geometry and geodesy (a branch of math that searches to determine the size and shape of earth, and the location of objects or areas on the earth) Books: Metrica, Automatopoietica, Pneumatica, Belopoeica, and Cheirobalistra. Inventions • • • He created a water organ, fire engine, coin operated device, and the aeolipile. Aeolipile: rotary steam engine that consisted of a sphere mounted on a boiler and having two nozzles to produce a rotary motion from the escaping steam. The siphon, known as Hero's foundation, was an instrument that produces a vertical jet of water by air pressure. Heron's Fountain