Energy Flow
advertisement

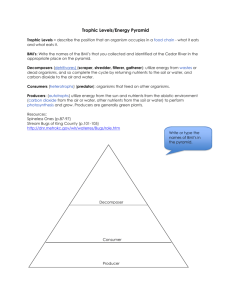
Energy Flow EQ: How does energy flow through living systems? Interactions and Interdependence Ecology: the interaction between animals and the environment The earth can be divided into different levels of organization Producers Defined as something that produces or converts energy from the sun into energy that animals can use Another term for these organisms is autotrophs These organisms perform photosynthesis and are the basis for the food chains Photosynthesis The process by which plants convert the sun’s energy to sugar with the help of carbon dioxide The bi-product of this process is oxygen Consumers An organism that consumes (eats) energy produced by plants or other animals Another term for these organisms is heterotrophs Different Types of Consumers Herbivores: eat only plants Carnivores: eat only meat Omnivores: eat both plants and meat Detritivores: feed on the remains of other organisms Decomposers: break down dead material Food Chains Show the flow of energy between organisms Only one possible prey item shown at each level Simplest way to show interactions Example of a Food Chain Phytoplankton Zooplankton Angel Fish Sea Turtle Food Web Shows the flow of energy between all members of an ecosystem Shows complex interactions Allows one to see what would happen if one species is removed Food Web Food Pyramid Each organism on the food chain is placed into a different trophic level The organism with the most energy is placed on the bottom and the organism that receives the least energy is placed on top Shows the loss of energy as you go up the food chain from plants to top predators Ecological Pyramids Pyramid of Numbers Shows the relative number of individual organisms at each trophic level. Biomass Pyramid Represents the amount of living organic matter at each trophic level. Typically, the greatest biomass is at the base of the pyramid. Energy Pyramid Shows the relative amount of energy available at each trophic level. Organisms use about 10 percent of this energy for life processes. The rest is lost as heat. Food Pyramid Food Pyramid Layers The bottom level of a food pyramid are the primary producers The plants and algae that perform photosynthesis to convert the suns energy to chemical energy The second level are the primary consumers These are the organisms that eat the producers These organisms are called herbivores Food Pyramid Layers The next level contains the secondary consumers These are the organisms that eat the primary consumers These animals are considered carnivores if there diet is strictly other animals or omnivores if they also include plants in their diet The top level is the tertiary consumers These animals eat the secondary consumers Usually the top predators in an ecosystem Example of a Food Pyramid Tertiary Consumer Secondary Consumer Primary Consumer Producer Sea Turtle Angel Fish Zooplankton Phytoplankton Energy Transfer Only 10 percent of the energy is transferred between levels This is because an animal needs to expend energy in order to capture and eat its prey If it is taking too much energy to capture the prey than the animal will abandon the hunt (cheetah and gazelle) If there was 1000kg of energy at the producer level than the top predator would only get 1 kg Energy transfer 1 kg Of energy 10 kg Of energy 100 kg Of energy 1000 kg Of energy Sea Turtle Angel Fish Zooplankton Phytoplankton Explains why a sea Turtle must eat so much To survive